Understanding DNSSEC: A Key to Enhancing Internet Security
DNSSEC – The Domain Name System (DNS) is one of the most critical components of the internet. It acts as the “phonebook” of the internet, translating human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into machine-readable IP addresses. However, despite its importance, DNS has some inherent security weaknesses that can be exploited by cybercriminals. One such vulnerability is the risk of DNS spoofing or cache poisoning, where attackers trick DNS servers into delivering fraudulent responses. To address these threats, DNSSEC (Domain Name System Security Extensions) was introduced.
In this blog, we will explore what it is, how it works, and why you should consider implementing it for your domain.
What is DNSSEC?
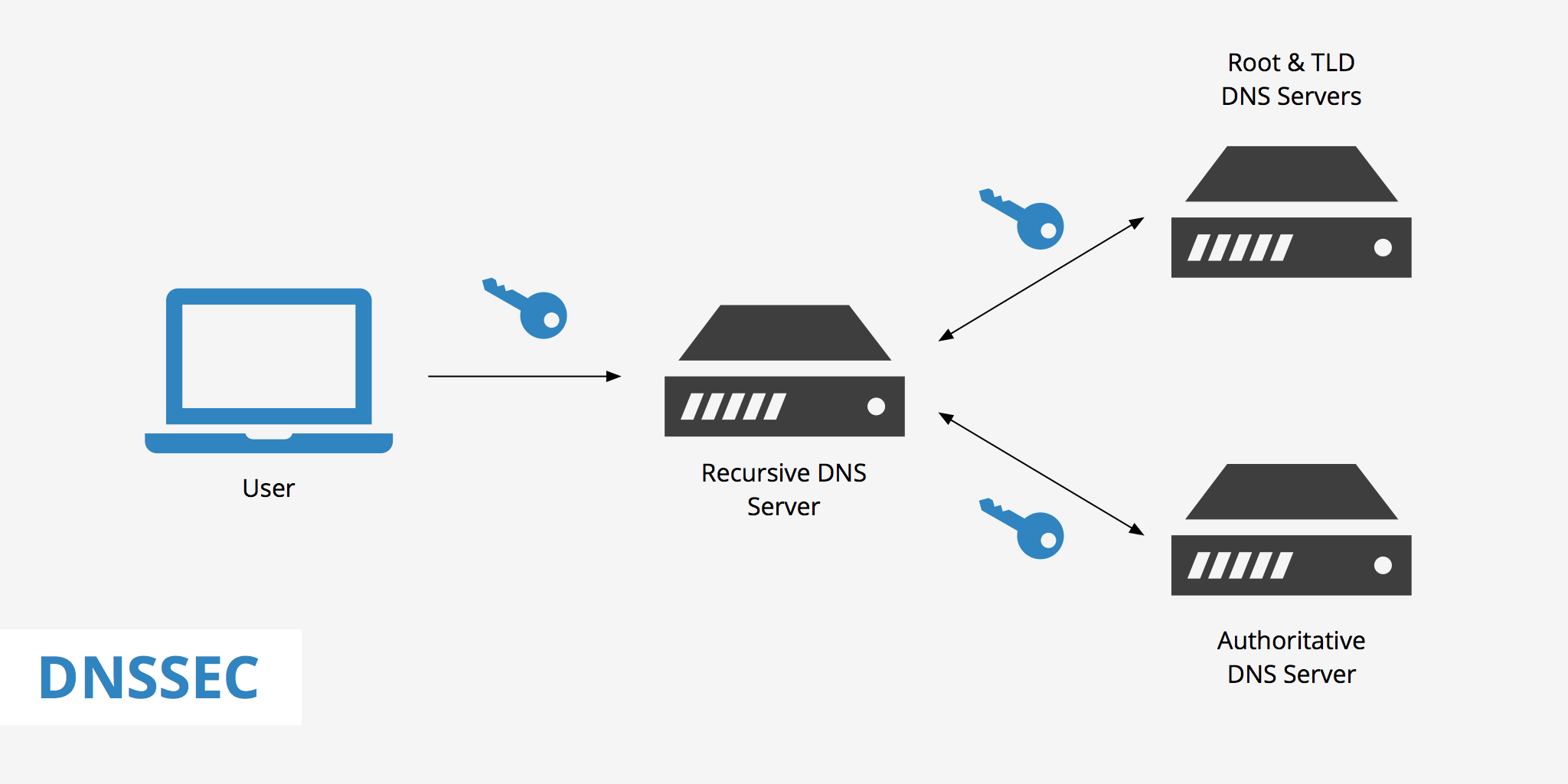
DNSSEC is a set of security extensions designed to protect DNS from attacks. It adds a layer of cryptographic signatures to DNS records, ensuring that the data received from DNS servers is authentic and has not been tampered with. In simpler terms, it helps to verify that the DNS response you’re getting is the legitimate one.
How Does it Work?
At the core of DNSSEC is the use of digital signatures and public key infrastructure (PKI). When a domain is configured with this, its DNS records (like A, MX, and TXT records) are signed with a private key. This signed record can then be verified using a corresponding public key. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Signing DNS Records: The domain owner uses a private key to sign the DNS records.
- Publishing the Public Key: The corresponding public key is made available in the DNS so that anyone querying the domain can verify the authenticity of the records.
- Validation: When a DNS query is made, the DNS resolver checks the DNS response using the public key to ensure the response has not been altered.
This process creates a chain of trust, starting from the root DNS servers down to individual domain names. If any part of the chain is tampered with, the DNSSEC validation will fail, alerting the user that the DNS response cannot be trusted.
Why is DNSSEC Important?
- Prevents DNS Spoofing and Cache Poisoning: One of the most significant risks in DNS is that attackers can manipulate DNS records and redirect users to malicious websites. It prevents this by ensuring that the DNS data is valid and hasn’t been tampered with.
- Protects Against Man-in-the-Middle Attacks: Without this, attackers can intercept and modify DNS queries, leading to man-in-the-middle attacks. It ensures that the communication between DNS resolvers and servers is secure.
- Improves Trust and Security: For businesses, especially those handling sensitive information, it provides an extra layer of security to prevent cyberattacks. It adds credibility and trust, particularly for websites with online transactions, banking services, and other sensitive activities.
- Ensures Data Integrity: It guarantees that the data received from a DNS query is exactly what was intended. This is critical for the integrity of online communications, preventing fraud or redirection to fake sites.
How to Implement DNSSEC
Implementing DNSSEC for your domain requires a few steps:
- Check DNSSEC Support: First, ensure that your domain registrar and DNS hosting provider support DNSSEC.
- Sign Your Domain’s Zone: If you’re managing your own DNS, you will need to configure DNSSEC for your domain’s DNS zone by signing it with a private key.
- Publish DS Records: After signing your domain, you need to publish Delegation Signer (DS) records with your registrar to link your domain’s DNSSEC setup with the global DNS infrastructure.
- Monitor DNSSEC: Once implemented, you should regularly monitor your domain’s DNSSEC status to ensure everything is functioning as expected.
Common Challenges with DNSSEC
While it offers significant security benefits, there are some challenges to consider:
- Complex Setup: Configuring it correctly can be complex and requires a solid understanding of DNS and cryptography.
- Compatibility Issues: Some older systems or DNS resolvers might not support DNSSEC, which could cause issues for users accessing your site.
- Performance Overhead: DNSSEC introduces additional checks and signatures, which could slightly impact the performance of DNS queries. However, this is typically negligible and worth the added security.
Conclusion
In an increasingly digital world where cyber threats are ever-present, securing your online presence is more critical than ever. It provides an essential layer of protection for your domain by ensuring that your DNS records are authentic and untampered with. While it may require some initial setup and technical knowledge, the benefits of implementing it far outweigh the risks of leaving your domain vulnerable to cyberattacks.
If you haven’t already, consider enabling it for your domain to enhance its security and protect your users from malicious activities.